
Every day, we are creating1 2.5 quintillions(1018) bytes of data, out of which 90 percent of the data in the world has been created in the last two years alone. This massive amount of data is generated every now and then by millions of devices around us and with various social networking websites.
Data can be transformed into meaningful insights to help organizations in taking crucial decisions in their business by extracting valuable data-driven insights from the tremendous amount of data present in the world. It helps them creating value-added data products.
The person who generates valuable insights and patterns from the data is called Data Scientist. No wonder why it is an important asset for the company as regarded as one of the important jobs of the century.
The term data science became very difficult to explain especially in today world. “Data science is an interdisciplinary field that uses scientific methods, processes, algorithms, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from data in various forms, both structured and unstructured, similar to data mining.” —Wikipedia2.
In other words, it is a set of fundamental principles that guide the extraction of knowledge of data.
A very good explanation of the word data science is explained by Drew Conway’s Data Science Venn Diagram3 on his blog.
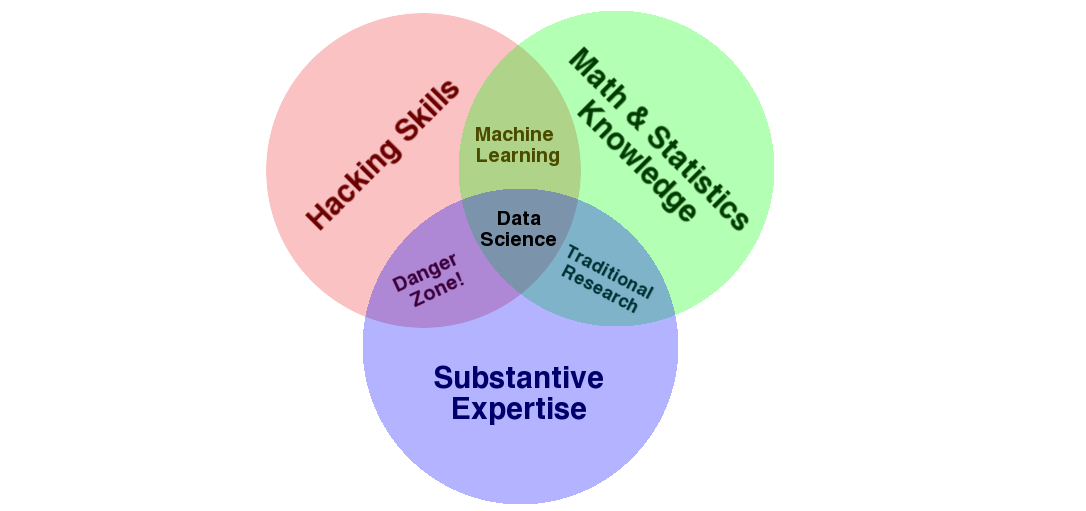
Based on this diagram, which captures the spirit of the word “data science”, it comprises of three different kinds of knowledge:
1.Statistics: For modeling and summarizing datasets (which are increasing day by day).
2.Computer knowledge: For gathering, processing and visualizing the data (designing and using the algorithms).
3.The domain expertise: For expressing the correct questions and to put their answers in context.
As it can be seen that, these are not a new domain of knowledge to learn but a new set of skills are required which are easy to learn.
Why Python is used for Data Science
Python is an open source high-level language. It has powerful computation tools and packages which make it easy to focus on the task. When we execute Python code, the Python interpreter converts your code into bytecode that your computer can understand, and then runs that bytecode. Python is a high-level language. High-level languages allow you to write programs faster as the interpreter makes the decisions on how to execute your instructions Following are some of the reasons for choosing Python for Data Science projects.
Easy to learn: Python is a simple scripting language that makes it easy to interact with data that makes it learning curve easy.
Open source: Python is free and open source, which means Python source code is available for the public and anyone can contribute to its development.
Active community: Python has a large and active scientific community so it is easy to get help.
Scalable: It is fast and scalable as compared to other languages like R, Stata, Matlab.
Packages: Wide range of packages that make it easy to get started and build the application. Some of them are:
- NumPy for manipulation of homogeneous array-based data.
- Pandas for manipulation of heterogeneous and labeled data.
- SciPy for common scientific computing tasks.
- Matplotlib for publication-quality visualizations.
- Scikit-Learn for machine learning.
- IPython for interactive execution and sharing of code.
It allows the programmer to focus on the task at hand very fastly.
Data science Project Overview
Here are the main steps you will follow for any data science project.
-
Ask questions: Ask question what do you want to analyze. Talk with the business unit to figure out the questions. Either you have given data and you ask the question based on it or first, you ask the question and then gather data based on your it.
- Data Wrangling: Once you have clear questions in your mind, now you can proceed to data wrangling which has three steps:
- Gather data: Either data is provided from the business unit or need to gather from different sources which generally comes in various formats.
- Assess the data: Once you gather the data, now you will make sure if the data have any problems like not in the same format or if there are any other problems.
- Cleaning the data: It is very rare that the data one get is clean. Most of the time, of a data science project, is spent on cleaning the data. It is done either by modifying it to new data or by removing the duplicates or unnecessary data as well as fixing the missing data.
-
Exploratory Data Analysis(EDA): In this step. you explore the data, find patterns, relationships by visualizing the data which helps to gain insights. Feature engineering (removing outliers and creating better features) is also done in this process. After this, we select a model and train it. This is a repetitive process.
- Present the solution: Present the insights which you gained from the data. It could be done in the form of reports, blog posts, presentations, etc.
Prepare the data science environment in three steps
Jupyter
For new users, it is recommended to install Anaconda4, the most popular python data science platform. Anaconda installs Python, Jupyter Notebook and other packages used for data science. Learn more about Jupyter here.
 Download Anaconda for Python 3
Download Anaconda for Python 3
Project template
It is a good practice to have a project template which makes it easy to work and understand. A Cookiecutter is a logical, reasonably standardized, but flexible project structure for doing and sharing data science work. It can be installed by the following command.
$ pip install cookiecutter
 Installing Cookiecutter
Installing Cookiecutter
Once it is installed we can create a project template by the following command.
$ cookiecutter https://github.com/drivendata/cookiecutter-data-science
 Creating project template Cookiecutter
Creating project template Cookiecutter
Git
Versioning system is important for any data science project. It helps in working together as well as going back to the earlier version if there are any problems. We will be using Git in our case. We don’t need to have the expertise to use git, just knowing 4 commands will suffice in this project.
git init: Initialize the git repository.git add: Add files in git. For adding all the files of this current folder to the git system we have to add a dot(.) after this command.git commit: Commit the changes using the command. This tells the git that we have committed our changes and can create our checkpoints. It’s a good practice to provide commit messages for referencing by adding a-mflag with it.git log: It shows all the logs. But to have only one line use---onelinewhich shows git message with git commit id.
 Basic git commands for data science projects
Basic git commands for data science projects
Conclusion:
In this post, you learned about Data Science and learn why Python is preferred for it. We also explored different steps for starting data science projects and finally, we saw the environment which is required for a data science project. I hope it helps to understand some basics concepts of data science. In the coming tutorials, we will explore more about data science and the various algorithm used for it, till then explore more go through the references.
References and further reading list
1: https://www-01.ibm.com/common/ssi/cgi-bin/ssialias?htmlfid=WRL12345USEN
2: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_science
3: http://drewconway.com/zia/2013/3/26/the-data-science-venn-diagram
4: https://www.anaconda.com/
5 Python Data Science Handbook: Essential Tools for Working with Data (English Edition)
Leave a comment